 5FISH
5FISH
Around 450 million years ago, the first fish appeared on the scene. Today, there are roughly 34,000 different species of fish with about 250 new species identified each year. Almost half of all fish species live in freshwater.
Evolution: The Transition from Worms to Fish
A worm-like creature called the Pikaia likely helped make the transition from worms to fish. The main feature that made this worm species different was a nerve cord that ran the length of its body. This creature had a distinct head, mirror symmetry, v-shaped muscles and a nerve cord that ran the length of its body, the forerunner of the backbone. The Pikaia looked like a worm and swam like an eel. A sturdier structure and the ability to move through the water and change direction much more quickly than worms are among the survival advantages that evolution gave fish.
Fish: First Backbone
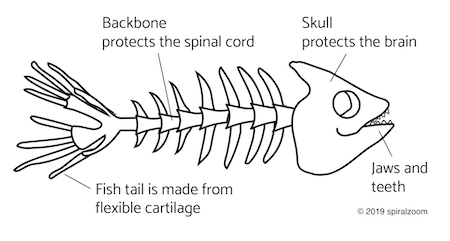 The fish had a brain that was wired to a spinal cord, in the same way your body is supported by a backbone. The backbone also provides a structure for the evolving nervous system. The spinal cord links the nervous system to the brain.
The fish had a brain that was wired to a spinal cord, in the same way your body is supported by a backbone. The backbone also provides a structure for the evolving nervous system. The spinal cord links the nervous system to the brain.
All animals with backbones are descended from fish. They’re all known as vertebrates.
Backbones help increase swimming speed. With a backbone you can make sharp turns and plot your course through the water.
Fish: Body Plan
Fish inherited their basic body structure from their worm-like ancestors, with the brain connected to a mouth, eyes and digestive system.
Fish: Brains and Eyes
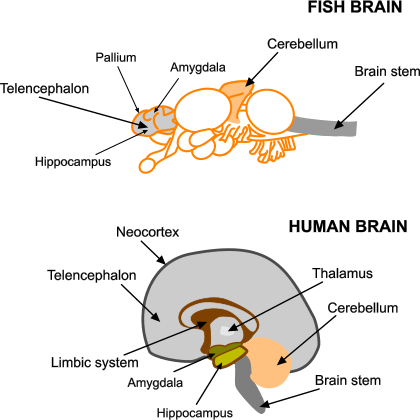
Fossil evidence suggests a strong connection between the evolution of eyes and brains. Once a creature can see, it can more easily find mates, locate food and avoid predators.
Fish: Oxygen Power
The rapid co-evolution of eyes, brains and bones, corresponded with the leap in oxygen levels in the atmosphere during the Cambrian Explosion. Scientists feel that this increase in oxygen levels provided a big boost for evolution.
Oxygen is fuel to our cells. With more oxygen available, animals could develop new, fuel-guzzling body parts.
Suddenly living things had great opportunities to evolve in ways never seen before. It was like a gold rush where many new species struck it rich and were able to build elaborate new body parts!
Fish: Blood
Fish were also our first ancestor with a circulatory system, a heart that pumps blood through a highway of arteries and veins.
Most fish hearts have two chambers along with an entrance and an exit.
What do You have in Common with Fish?
From your ancestors the fish you inherited bones and muscles. Like fish you also have jaws and teeth. Fish have well developed vision. Although vision started with eyespots in the worm, our ancestors the fish evolved a much more well developed visual system. Many aspects of our eyesight are a gift from the fish.
What's Next?
A branch of the fish family split off and eventually evolved into a reptile.
Learn More:
Your Inner Fish: PBS show
http://www.pbs.org/your-inner-fish/
Great timeline diagram of fish evolution
https://www.fishkeepingworld.com/evolution-of-fish/#The_First_Fish_Cambrian_Period
Six Traits humans inherited from fish
http://mentalfloss.com/article/55869/6-traits-humans-inherited-fish
Nine ways fish are like humans
https://www.peta.org/features/ways-fish-just-like/
